Comparing Natural Stone to Artificial Materials
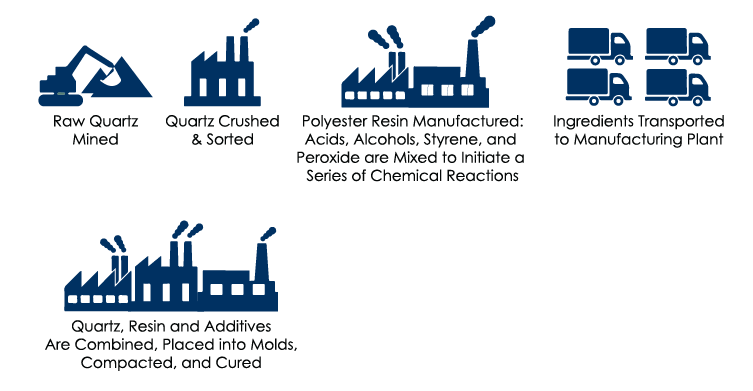
To understand how natural stone can help to reduce the embodied carbon of building projects, review the infographics below that detail the steps in the manufacturing process for natural stone, precast concrete cladding, terrazzo flooring, and engineered quartz countertops. It is easy to understand why natural stone’s global warming potential is lower than those materials whose manufacturing processes are more complex and include multiple ingredients.
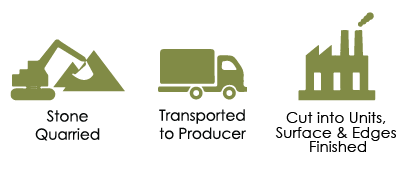
Natural Stone
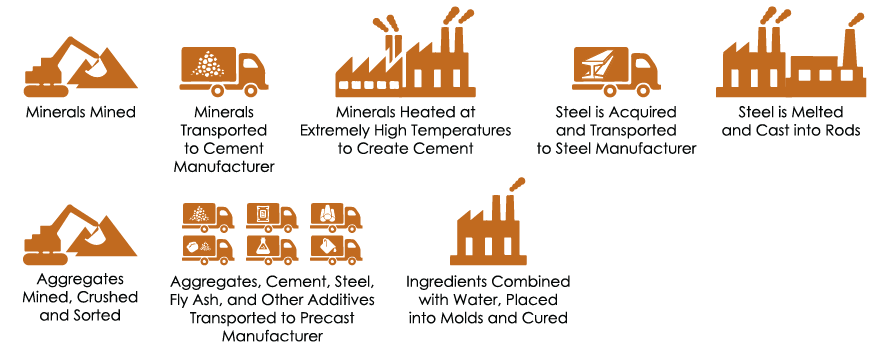
Precast Concrete Cladding
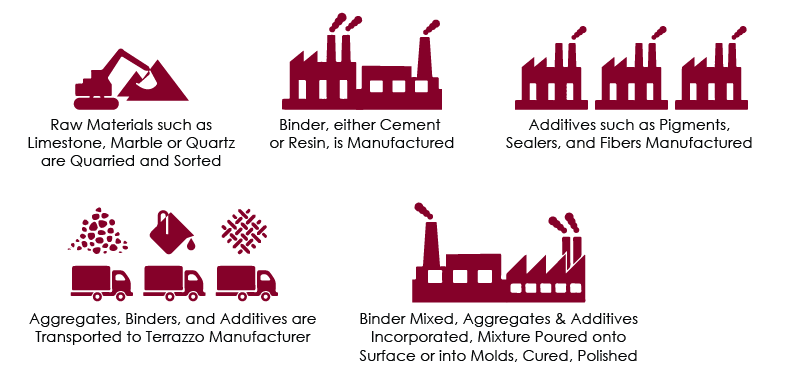
Terrazzo Flooring
Engineered Quartz Countertops
Embodied Carbon Comparisons
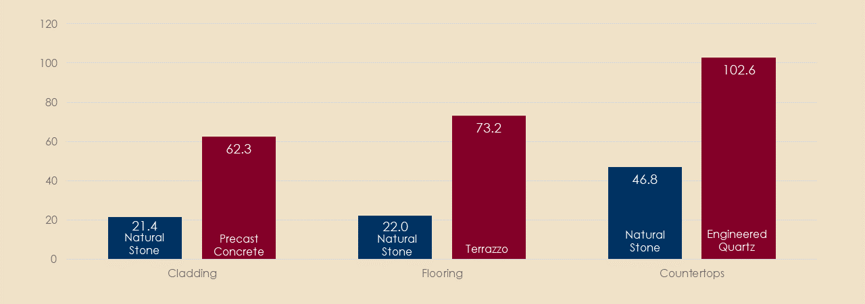
The embodied carbon quantities displayed were estimated based on the following:
Unite of Measure: Global Warming Potential (kg CO2 eq)
Functional Unit: 1m2
Scope: Raw Material Extraction, Transportation, Manufacturing (A1-A3)
Natural Stone: Industry-Wide EPDs for Cladding, Flooring & Countertops
Pre-Cast Concrete Cladding: Industry-Wide EPD for Architectural Precast Panels, 150 lbs per ft3
, 4” thick
Engineered Quartz: Average of three individual manufacturer EPDs including Corian Quartz, Vicostone,
and Lotte
Terrazzo: Average of three individual manufacturer EPDs including Compac, Sensitile, and Sherwin
Williams
To help quantify the embodied carbon of natural stone, the Natural Stone Institute published a set of Industry-Wide Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs). The disclosures include cradle to grave life cycle impacts for cladding, flooring, countertops. The Industry-Wide EPDs published were funded in part by the Natural Stone Foundation, the philanthropic arm of the Natural Stone Institute.
The above document is an extraction from: National Stone Institute.